ServiceAccount 周りの知識を整理しましたので、知識ポイント抜粋するような形で覚えておきたいポイントをできるだけ箇条書きで記載しました。
多少読みずらいところがありますが、メモとして後で思い出す時に使いやすいかと思います。
まず初めに、以前で紹介した記事の説明図を載せておきます。
詳細の仕組みを後続の内容で紹介するのですが、この図を見ながら、少しずつイメージを形成していただければと思います。
ServiceAccount仕組みの関係図
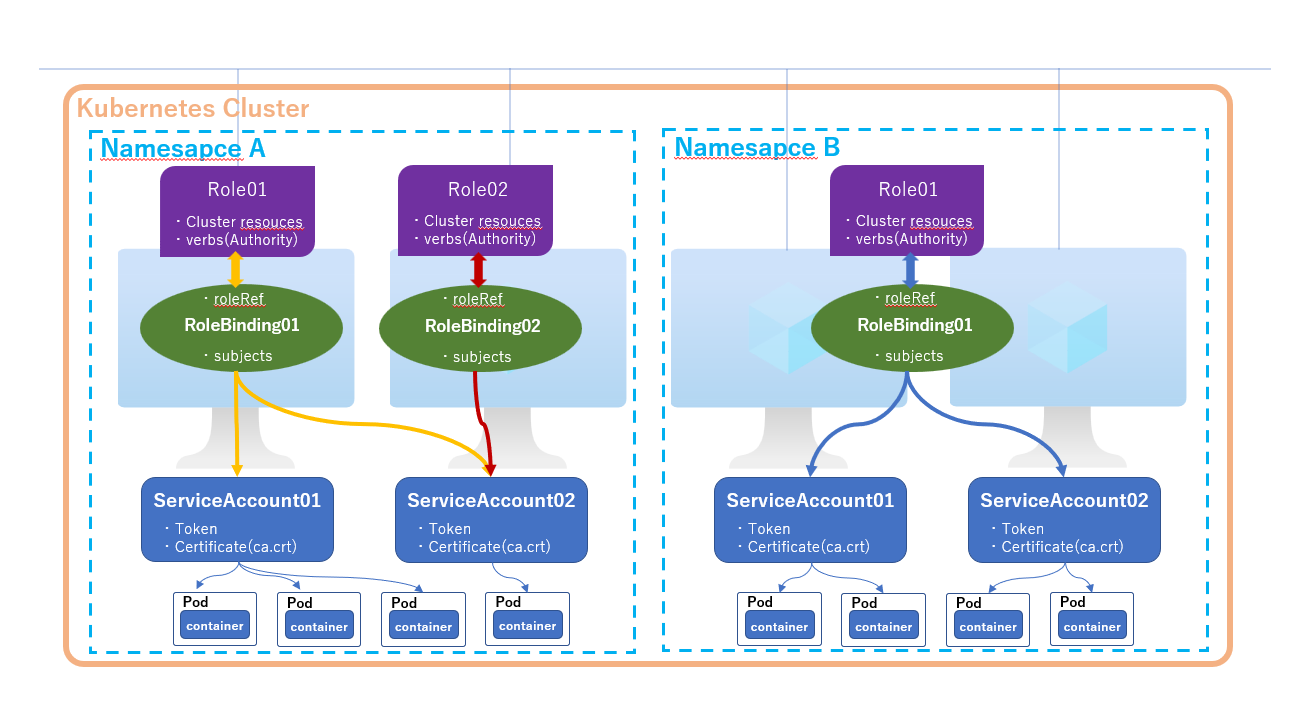
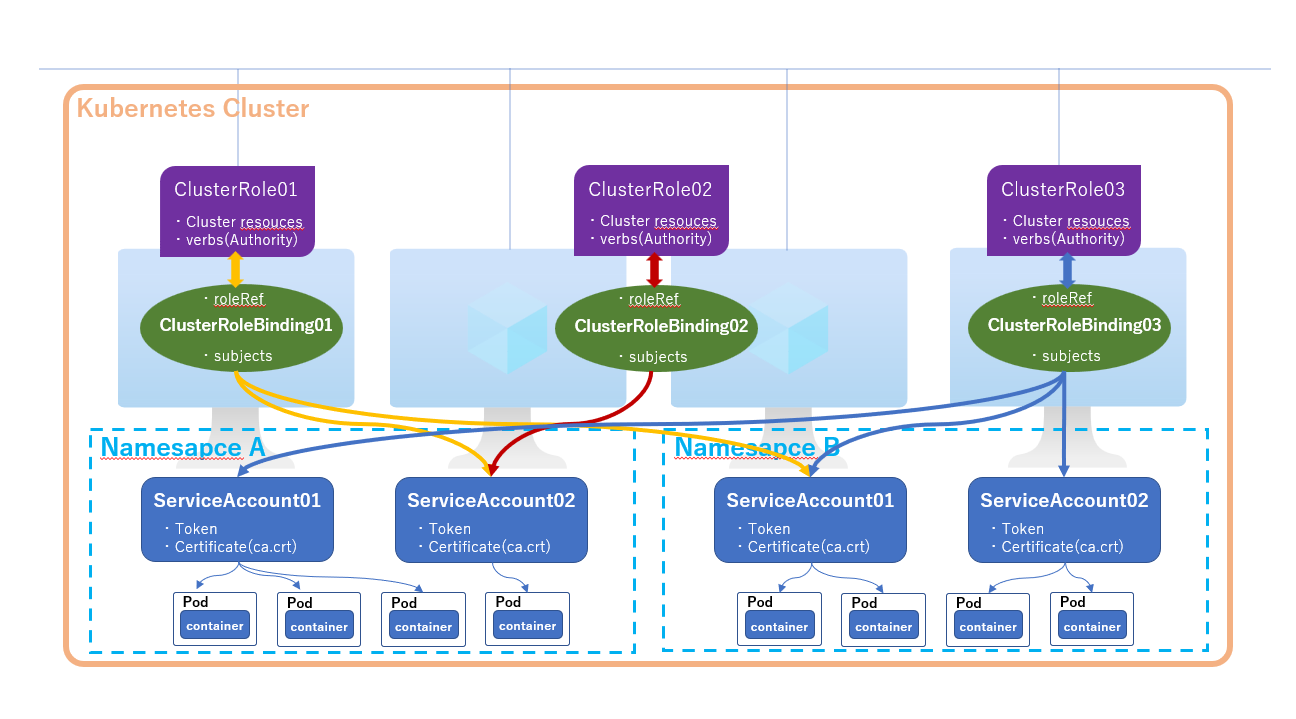
仕組みの理解をイメージしやすいよう、以下の図を作成しました。
簡単にイメージ作りに役に立ってればと思います。
Roleのイメージ図
ClusterRoleのイメージ図
ServiceAccount
では、ServcieAccount から紹介していきたいと思います。
ServcieAccount の特徴:
-
ServcieAccount は、Kubernetes のユーザー タイプの 1 つ
- AKS のユーザー タイプ:UserAccount、ServcieAccount
-
ServiceAccount は Namespace 指定で作成する
- Namespace 所属のリソース
- 作成は他の K8s リソースと同様にマニフェストで作成可能
-
ServcieAccount は、K8s のリソースで、API サーバーにリクエストを出す時の認証/認可で使用される
- 使用例:Pod で直接 K8s のリソースを操作する時とか
- 設定:Pod などのマニフェストで、ServcieAccount を定義可能
-
K8s のリソースで、ServcieAccount を指定しない場合、デフォルトの ServcieAccount が使用される
- デフォルト ServcieAccount 名:default
- デフォルト ServcieAccount は Namespace ごとに既定で作成される
-
ServcieAccount はトークン ベースでの認証が行われる
- ServcieAccount が作成されたら、自動的にトークン (secret) が作成される
- ServcieAccount の資格情報 (トークン) は Kubernetes シークレットとして保管されている
- 承認された Pod が API サーバーと通信する際に、トークンを使われる (トークンや証明書の場所をマウントして使う)
- Pod などで、ServcieAccount を指定すると既定では自動的にトークンをマウントする
- 自動マウントさせない設定も可能 (ServcieAccount 又は Pod で設定可能:
automountServiceAccountToken: false※ Pod の設定が優先) - トークンを変更したい場合、該当の secret を削除することで、自動再作成される
-
AKS のユーザー タイプ:
- UserAccount:クラスタ レベル ユーザー (Azure AD などのサービスで管理)
- ServcieAccount:Namespace レベル ユーザー (Kubernetes で管理)
ServcieAccount の作成と確認
ServcieAccount のマニフェスト例:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: sample-serviceaccount # ServcieAccount 名
namespace: default # 所属の Namespace 指定
secrets: # 含まれる権限トークンの secret を配列で指定 ※ secret は別途作成が必要
- name: xxx
- name: yyy
# imagePullSecrets: # イメージダウンロード用認証情報を取得
# - name: xxxServcieAccount 指定の Pod のマニフェスト例:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment # Deployment名
labels:
app: nginx
spec: # ReplicaSetの設定
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template: # Podの設定
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
serviceAccountName: sample-serviceaccount # ServcieAccount 指定
containers: # コンテナの設定
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80ServcieAccount の確認:
kubectl get pods <pod名> -o yaml コマンドで、ServcieAccount の設定を確認できます。
また、Pod にマウントした証明書やトークンのパスも確認できます。
※ 下記の例は default ServcieAccount を使う時の出力です。
※ pod にログインして、パスを確認することも可能です。
$ kubectl get pods nginx-deployment-585449566-kcl4n -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
...
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:latest
...
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount
name: kube-api-access-dw55p
readOnly: true
...
securityContext: {}
serviceAccount: default
serviceAccountName: default
...Role と ClusterRole (RBAC)
ServiceAccount の権限設定では、Role という権限を定義するリソースを使って設定もできます。
Role は権限の影響範囲で、以下の2種類があります。
- Role:Namespace範囲 (Namespace 指定して作成する)
- ClusterRole:クラスタ全体 (Namespace指定不可)
また、ServiceAccount と Role を紐付けするために、以下の Binding 用のリソースも必要です。
- RoleBinding:ServiceAccount と Role の紐付け
- ClusterRoleBingding:ServiveAccount と ClusterRole の紐付け
K8s では、デフォルトで用意されているシステムのロールが存在します。
ただ、一般的によく知られているのは以下の幾つかのユーザー向け Role です。
cluster-admin:Super User、任意のリソースで任意のアクションを実行できます。ClusterRoleBinding:クラスター内およびすべての Namespace 内のすべてのリソースを完全に制御可能RoleBinding:Namespace 自体を含む、RoleBinding の Namespace 内のすべてのリソースを完全に制御可能
admin:Namespace 内の管理者アクセス権限RoleBinding:Namespace 内に Role と RoleBinding を作成する機能を含め、Namespace のほとんどのリソースへの読み取り/書き込みアクセスを許可- リソース クォータまたは Namespace 自体への書き込みアクセスは許可しない
edit:Namespace 内のほとんどのオブジェクトへの読み取り/書き込みアクセスを許可- RoleまたはRoleBindingの表示または変更を許可しない
view:Namespace 内のほとんどのオブジェクトを表示するための読み取り専用アクセスを許可
確認するには、以下のコマンドを使用できます。(AKSの結果)
Role
~$ kubectl get role -A
NAMESPACE NAME CREATED AT
kube-public system:controller:bootstrap-signer 2022-05-02T03:08:19Z
kube-system extension-apiserver-authentication-reader 2022-05-02T03:08:19Z
kube-system system::leader-locking-kube-controller-manager 2022-05-02T03:08:19Z
kube-system system::leader-locking-kube-scheduler 2022-05-02T03:08:19Z
kube-system system:controller:bootstrap-signer 2022-05-02T03:08:19Z
kube-system system:controller:cloud-provider 2022-05-02T03:08:19Z
kube-system system:controller:token-cleaner 2022-05-02T03:08:19Z
kube-system tunnelfront-secret 2022-05-02T03:08:40ZClusterRole
~$ kubectl get clusterrole -A
NAME CREATED AT
admin 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
aks-service 2022-05-02T03:08:36Z
cloud-node-manager 2022-05-02T03:08:35Z
cluster-admin 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
container-health-log-reader 2022-05-02T03:08:39Z
csi-azurefile-node-secret-role 2022-05-02T03:08:39Z
edit 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
node-viewer 2022-05-02T03:08:40Z
omsagent-reader 2022-05-02T03:08:36Z
system:aggregate-to-admin 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:aggregate-to-edit 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:aggregate-to-view 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:auth-delegator 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:azure-cloud-provider 2022-05-02T03:08:39Z
system:azure-cloud-provider-secret-getter 2022-05-02T03:08:39Z
system:basic-user 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:certificates.k8s.io:certificatesigningrequests:nodeclient 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:certificates.k8s.io:certificatesigningrequests:selfnodeclient 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:certificates.k8s.io:kube-apiserver-client-approver 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:certificates.k8s.io:kube-apiserver-client-kubelet-approver 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:certificates.k8s.io:kubelet-serving-approver 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:certificates.k8s.io:legacy-unknown-approver 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:attachdetach-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:certificate-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:clusterrole-aggregation-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:cronjob-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:daemon-set-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:deployment-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:disruption-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:endpoint-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:endpointslice-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:endpointslicemirroring-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:ephemeral-volume-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:expand-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:generic-garbage-collector 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:horizontal-pod-autoscaler 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:job-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:namespace-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:node-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:persistent-volume-binder 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:pod-garbage-collector 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:pv-protection-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:pvc-protection-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:replicaset-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:replication-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:resourcequota-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:root-ca-cert-publisher 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:route-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:service-account-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:service-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:statefulset-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:ttl-after-finished-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:controller:ttl-controller 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:coredns 2022-05-02T03:08:39Z
system:coredns-autoscaler 2022-05-02T03:08:39Z
system:discovery 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:heapster 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:kube-aggregator 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:kube-controller-manager 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:kube-dns 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:kube-scheduler 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:kubelet-api-admin 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:metrics-server 2022-05-02T03:08:36Z
system:monitoring 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:node 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:node-bootstrapper 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:node-problem-detector 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:node-proxier 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:persistent-volume-provisioner 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:persistent-volume-secret-operator 2022-05-02T03:08:36Z
system:prometheus 2022-05-02T03:10:49Z
system:public-info-viewer 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:service-account-issuer-discovery 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
system:volume-scheduler 2022-05-02T03:08:18Z
view 2022-05-02T03:08:18ZRole の作成
Role の作成もほかの K8s リソースと同じく、マニフェストで定義できます。
Role マニフェスト例:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: default # Namespace 指定
name: pod-reader # Role の名前
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" はコアのAPIグループに属するリソース
resources: ["pods"] # 対象のリソース種類を指定
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"] # 実行できる操作に指定 ※ 指定できる操作は後述ありRole の特徴:
namespaceの指定が必要apiGroups何を入れるべきかkubectl api-resourcesコマンドで、リソース種類のapiGroupsが表示されている- 複数
apiGroupsのリソースも存在する:Deployment はappとextensionsに属している - 特定の
apiGroupsに属していない場合はCore API groupを指定する:""が Core API group です。
verbsで指定できる操作*:すべての処理create:作成delete:削除get:(情報)取得list:一覧取得patch:一部設定変更update:更新watch:変更の追跡
Deployment マニフェスト例:
# APIグループ" extensions "と " apps " の両方で、Deployments への読み取り/書き込みを許可
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: default
name: deployment-full-role
rules:
- apiGroups: ["extensions", "apps"]
#
# HTTPレベルでの、Deployment にアクセスするリソースの名前
# オブジェクトは "deployments"
resources: ["deployments"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]※ 上記マニフェスト例の配列を yaml 形式で書いても問題ない
ClusterRole の作成
ClusterRole マニフェスト例:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
# 「namespace」は ClusterRoles が Namespace に属していないため、省略されています
name: deployment-read-role
rules:
- apiGroups: ["extensions", "apps"]
#
# HTTPレベルでの、Secretにアクセスするリソースの名前
# オブジェクトは"secrets"
resources: ["deployments"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"] # deployment に対する権限
- nonResourceURLs: ["/healthz", "/healthz/*"] # nonResourceURLの「*」はサフィックスグロブマッチです
verbs: ["get", "post"] # nonResourceURLs に対する権限ClusterRole の特徴:
namespaceの指定は不要apiGroups:※ Role と同じverbs:※ Role と同じnonResourceURLsの指定が可能nonResourceURLs:ヘルスチェックのエンドポイントやバージョン情報の表示用エンドポイントなどの URL- K8s に関する API ではない
- 例えば、Deployment に関して、Read ができる権限と
nonResourceURLsの Get 権限の ClusterRole で死活監視するとか
ClusterRole の Aggregation (集約)
複数の ClusterRole を1つの ClusterRole に集約 (関連付け) して、新しい ClusterRole を作成することもできます。
元の ClusterRole が変更された場合、集約の ClusterRole もその変更が反映されるようになっています。
※ 集約の ClusterRole に権限を設定しても、効果はないので、ご注意ください。
※ Role には集約できません
集約例:
# 元 ClusterRole 1
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
namespace: default
name: deployment-read-role
labels: # 集約するために設定した labels
app: sample-rbac
rules:
- apiGroups: ["extensions", "apps"]
resources: ["deployments"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
---
# 元 ClusterRole 2
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
namespace: default
name: services-read-role
labels: # 集約するために設定した labels
app: sample-rbac
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services"]
verbs: ["get"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: sample-aggregated-clusterrole
aggregationRule:
clusterRoleSelectors: # Labels で集約する
- matchLabels:
app: sample-rbac
rules: [] # コントロールプレーンは自動的にルールを入力するので、記載しても上書きされるRoleBinding と ClusterRoleBinding
RoleBinding と ClusterRoleBinding の構成はほぼ同じです。
roleRef で指定した Role を subjects で指定した User や ServcieAccount に binding (紐付け)します。
特徴:
- 1 RoleBinding に、1 Role だけですが、subjects には複数の User や ServcieAccount を指定可能
- 1 Role ⇔ 多 User
RoleBinding 例
# サンプル ServcieAccount 作成
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: sample-serviceaccount-1 # ServcieAccount 名
namespace: default # 所属の Namespace 指定
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: sample-serviceaccount-2 # ServcieAccount 名
namespace: default # 所属の Namespace 指定
---
# RoleBinding 作成
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: role-grantor-binding
namespace: default # RoleBinding は Namespace 指定必須
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: deployment-full-role # 上記の例で作った role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: sample-serviceaccount-1
namespace: default # ServcieAccount は Namespace 指定必須
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: sample-serviceaccount-2
namespace: default結果確認:
~$ kubectl get rolebindings -o wide
NAME ROLE AGE USERS GROUPS SERVICEACCOUNTS
role-grantor-binding Role/deployment-full-role 98s default/sample-serviceaccount-1, default/sample-serviceaccount-2ClusterRoleBinding 例
# サンプル ServcieAccount 作成
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: sample-serviceaccount-3 # ServcieAccount 名
namespace: default # 所属の Namespace 指定
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: sample-serviceaccount-4 # ServcieAccount 名
namespace: default # 所属の Namespace 指定
---
# ClusterRoleBinding 作成
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: cluster-role-grantor-binding
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: deployment-read-role # 上記の例で作った ClusterRole
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: sample-serviceaccount-3
namespace: default # ServcieAccount は Namespace 指定必須
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: sample-serviceaccount-4
namespace: default結果確認:
~$ kubectl get clusterrolebindings cluster-role-grantor-binding -o wide
NAME ROLE AGE USERS GROUPS SERVICEACCOUNTS
cluster-role-grantor-binding ClusterRole/deployment-read-role 4m25s default/sample-serviceaccount-3, default/sample-serviceaccount-4 最後に
今回は K8s の世界の話のみを紹介してますが、Azure の AKS において、Azure の RBAC との連携も可能なので、次回はそこら辺を纏めようと思います。


コメント